ava-practice
Node.js测试框架
参见 https://www.nodeguy.com/test/ , 说的还是比较清楚的。
ava 是什么?
未来的测试运行器
https://github.com/avajs/ava
简单的说ava是mocha的替代品,
- es6语法支持更好,对aysnc/await有支持
- 执行效率更高,使用io并发,就必须保证测试的原子性
- 语义上更简单,集众家之长
虽然 JavaScript 是单线程,但在 Node.js 里由于其异步的特性使得 IO 可以并行。AVA 利用这个优点让你的测试可以并发执行,这对于 IO 繁重的测试特别有用。另外,测试文件可以在不同的进程里并行运行,让每一个测试文件可以获得更好的性能和独立的环境。在 Pageres 项目中从 Mocha切换 到 AVA 让测试时间从 31 秒下降到 11 秒。测试并发执行强制你写原子测试,意味着测试不需要依赖全局状态或者其他测试的状态,这是一件非常好的事情。
历史
- 从2014年11月19日开始,中间停了好多长时间, 2015年9月8号之后开始大量提交代码
为什么要用 AVA?
- 轻量和高效
- 简单的测试语法
- 并发运行测试
- 强制编写原子测试
- 没有隐藏的全局变量
- 为每个测试文件隔离环境
- 用 ES2015 编写测试
- 支持 Promise
- 支持 Generator
- 支持 Async
- 支持 Observable
- 强化断言信息
- 可选的 TAP 输出显示
- 简明的堆栈跟踪
测试用例与断言
测试是为了通过测试来验证功能是否正确的一种编程手段。
测试用例指的是针对某一种情况而编写的测试。
测试用例用来验证的测试工具方法称为断言。一般断言,返回值是的boolean值,可以是比较、是否为空,正则等。
下面给出最简单的AVA测试用例simple.js
'use strict'
import test from 'ava'
test('my test', t => {
t.is(3, 3)
})
先按照AVA模块
$ npm install --global ava
执行
$ ava -v simple.js
✔ my test
1 test passed [21:51:19]
这里的is方法就是断言,如果返回的是true,则测试通过,显示的就是绿色的,否则测试结果就是红色的。
下面给出一个错误的测试用例falt.js
'use strict'
import test from 'ava'
test('my test2', t => {
t.is(2, 3)
})
执行
$ ava -v falt.js
✖ my test2 2 === 3
1 test failed [22:06:06]
1. my test2
AssertionError: 2 === 3
Test.fn (falt.js:4:5)
这个时候就是错误的,测试没有通过,即输出结果是红色的。写测试的目的就是为了让它全是红色,修改了代码之后,立即跑测试,测试通过里再提交。如果测试没有通过,你就继续修改,直至变绿为止。
一般会把测试丢到npm scripts里
"scripts": {
"test": "ava -v simple.js"
},
执行
$ npm test
> getting-start@1.0.0 test /Users/sang/workspace/17koa/book-source/getting-start
> ava -v simple.js
✔ my test
1 test passed [21:52:56]
AVS VS Mocha

其实tj也蛮喜欢ava的

断言
ava支持的断言都比较简单,总体来说是抄自tap和tape,除了plan方法外。
- .pass([message])
Passing assertion.
- .fail([message])
Failing assertion.
- .truthy(value, [message])
Assert that value is truthy.
- .falsy(value, [message])
Assert that value is falsy.
- .true(value, [message])
Assert that value is true.
- .false(value, [message])
Assert that value is false.
- .is(value, expected, [message])
Assert that value is equal to expected.
- .not(value, expected, [message])
Assert that value is not equal to expected.
- .deepEqual(value, expected, [message])
Assert that value is deep equal to expected.
- .notDeepEqual(value, expected, [message])
Assert that value is not deep equal to expected.
- .throws(function|promise, [error, [message]])
Assert that function throws an error, or promise rejects with an error.
error can be a constructor, regex, error message or validation function.
Returns the error thrown by function or the rejection reason of promise.
- .notThrows(function|promise, [message])
Assert that function doesn't throw an error or promise resolves.
- .regex(contents, regex, [message])
Assert that contents matches regex.
- .ifError(error, [message])
Assert that error is falsy.
自定义断言
使用node.js sdk里默认的assert
import assert from 'assert';
test(t => {
assert(true);
});
使用chai断言库,支持3种风格
import test from 'ava';
var assert = require('chai').assert;
var expect = require('chai').expect;
var should = require('chai').should();
test('expect with chai', t => {
// typeof
expect('test').to.be.a('string');
expect({ foo: 'bar' }).to.be.an('object');
expect(null).to.be.a('null');
expect(undefined).to.be.an('undefined');
expect(new Error).to.be.an('error');
expect(new Float32Array()).to.be.a('float32array');
expect(Symbol()).to.be.a('symbol');
});
test('should with chai', t => {
var foo = 'bar'
var tea = {
flavors:[1,2,2]
}
foo.should.be.a('string');
foo.should.equal('bar');
foo.should.have.length(3);
tea.should.have.property('flavors')
.with.length(3);
});
test('assert with chai', t => {
var foo = 'bar'
var tea = {
flavors:[1,2,2]
}
assert.typeOf(foo, 'string');
assert.equal(foo, 'bar');
assert.lengthOf(foo, 3)
assert.property(tea, 'flavors');
assert.lengthOf(tea.flavors, 3);
});
hook
test方法默认是顺序执行,如果里面是顺序执行的,那么它是正常的。如果里面是异步方法呢?结果是test执行完了,而异步方法还在跑,这样的结果是,这个测试怎么跑都是正确的,因为没有走断言。。。。
演示代码如下
test('#register()', t => {
// 此方法是异步的,保存需要时间
user.save((err, u) => {
console.log(err)
console.log('u=' + u)
t.true(u.password.length > 50)
})
});
当test完成,user.save还没完成,结果0断言,测试结果显示成功。。。这是非常典型的例子。
最简单的回调,注意写法,test.cb意味着这是需要调用t.end()才能结束,对于测试异步方法非常好用
test.cb('#register()', t => {
// 此方法是异步的,保存需要时间
user.save((err, u) => {
console.log(err)
console.log('u=' + u)
t.true(u.password.length > 50)
t.end()
})
});
- t.end() 结束异步调用,仅仅在test.cb()方法里有效
下面例子中,保证在测试save方法之前,执行完成before。也就是说,执行before等待2秒,然后再开始跑其他测试。
test.before.cb((t) => {
setTimeout(() => {
t.end();
}, 2000);
});
test('#save()', t => {
let user = new User({
username: 'i5ting',
password: '0123456789'
});
user.save((err, u) => {
if (err) log(err)
t.is(u.username, 'i5ting');
});
});
其他cb方法可依此类推
Control flow
- Promise
- Generator
- Async/await
Promise 支持
If you return a promise in the test you don't need to explicitly end the test as it will end when the promise resolves.
test(t => {
return somePromise().then(result => {
t.is(result, 'unicorn');
});
});
Generator 函数支持
AVA comes with built-in support for generator functions.
test(function * (t) {
const value = yield generatorFn();
t.true(value);
});
具体在mongoose里的generator里使用
test('#save()', function * (t) {
var u = yield User.create(user)
t.is(u.username, 'i5ting');
});
测试console.log或者其他终端输出内容,推荐使用co-exec,然后将结果正则匹配就好了
import test from 'ava';
var exec = require('co-exec');
test('exec()', function * (t) {
var commit = yield exec('ls -alt|grep .gitignore|wc -l');
console.log(commit)
t.true(commit == 1);
});
test('exec2()', function * (t) {
var result = yield exec('ls -alt')
console.log(result.trim().match(/(gitignore)/))
t.true(result.trim().match(/(gitignore)/).length > 1);
t.regex(result, /(gitignore)/);
});
还有一个断言t.regex,不过不太容易判断
Async/await支持
AVA comes with built-in support for async functions (async/await).
test(async function (t) {
const value = await promiseFn();
t.true(value);
});
// async arrow function
test(async t => {
const value = await promiseFn();
t.true(value);
});
db
每次连接数据库成功后,最好是dropDatabase
var mongoose = require("mongoose");
// 核心代码,是否开启测试
mongoose.set('debug', false);
var db = mongoose.connect("mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/db_helloworld");
db.connection.on("error", function (error) {
console.log("数据库连接失败:" + error);
});
db.connection.on("open", function () {
console.log("数据库连接成功");
mongoose.connection.db.dropDatabase();
});
测试覆盖率
https://github.com/bcoe/nyc
Just install both:
$ npm install --save-dev nyc ava
They you can add this to package.json:
"scripts": {
"test": "nyc ava"
}
集成其他badge也很简单,看它的文档即可
http api测试
使用supertest配置express比较简单,配置koa稍微麻烦,可以使用superkoa,使用这个模块就可以普通的supertest一样了。
实例
var superkoa = require('superkoa')
test.cb("superkoa()", t => {
superkoa('./koa.app.js')
.get("/")
.expect(200, function (err, res) {
t.ifError(err)
var userId = res.body.id;
t.is(res.text, 'Hello Koa', 'res.text == Hello Koa')
t.end()
});
});
其他选型
编辑器上的test runner
wallabyjs
Intelligent and super fast test runner for JavaScript/TypeScript/CoffeeScript.
https://wallabyjs.com/
ext install wallaby-vscode
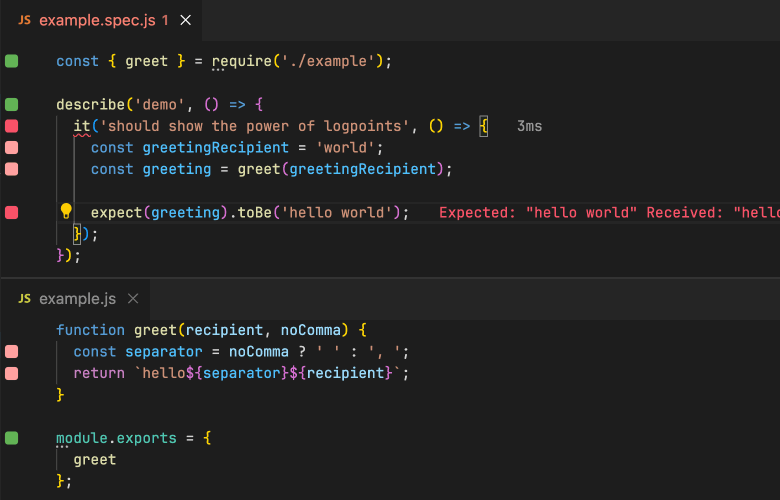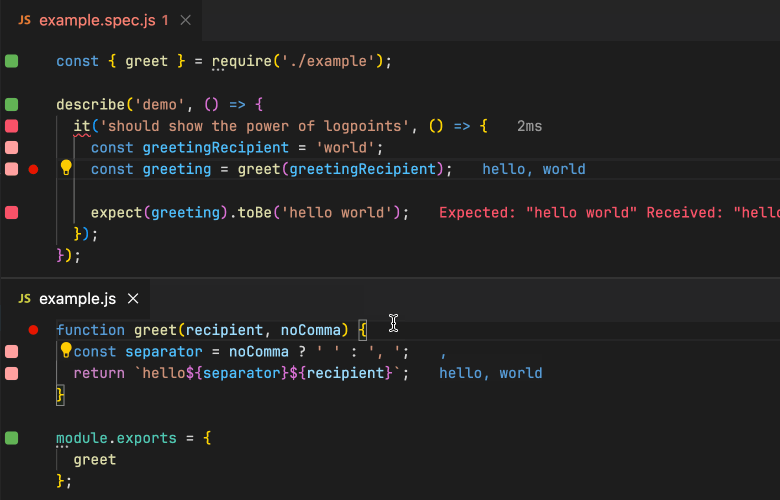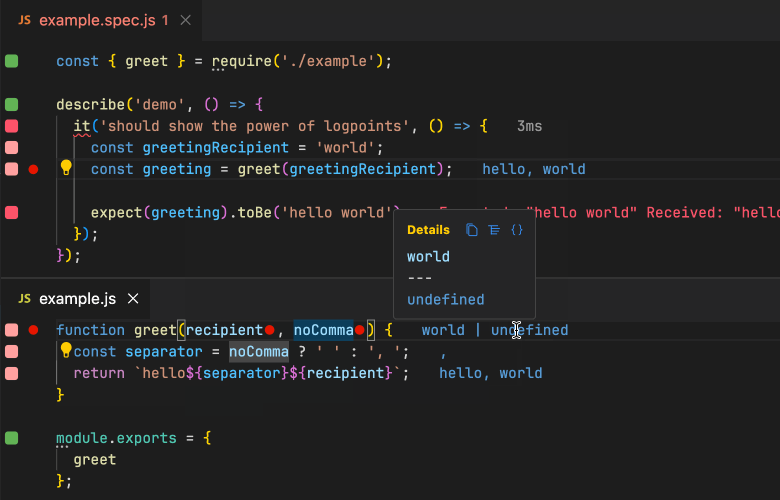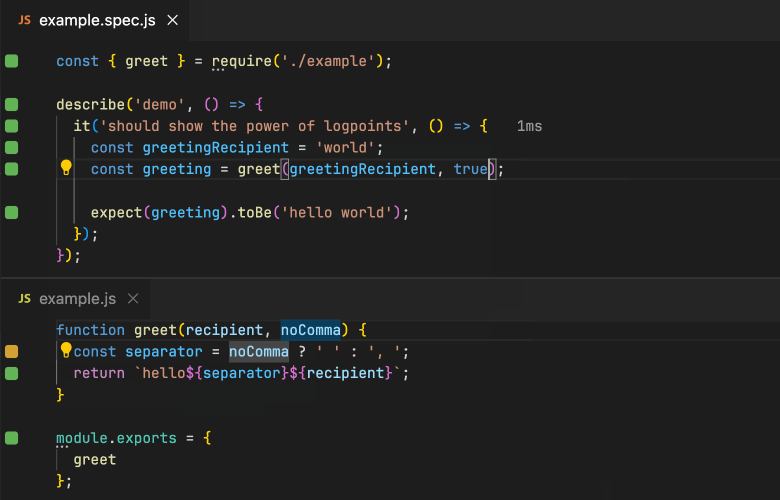
使用ava的开源项目推荐
找这类的项目最好是从ava开始,找贡献的相关作者,从这些作者的项目里找,基本上是十有八九。
FAQ
单元测试的测试用例,总是有种无从下手的感觉,有啥好的学习方法分享?
看每个模块的测试,然后照着写就好了
越小的模块的测试看着越简单,是入门佳品
把公司的项目写的像开源项目一样,先加测试,然后加ci,一步一步来就好了。
回复常见提问
我用了用 ava,感觉它的 test(xxx) 跟 mocha 的 describe it 相比还是描述性弱了点,就决定还是继续用 mocha 了。
而且要求全都可以独立执行,像 cnode 这种项目的测试代码,由于有些数据库状态需要保持,如果每个 case 都能保证独立运行的话,要花的工夫不少,还不如 mocha 那种顺序执行,然后 test 跟 test 之间存在依赖关系。
一些小的地方我也用过 ava,当对同一个函数,传入三种不同参数的时候(正常,失败,异常)的时候,test(xxx) 感觉不好写。
现在如果我写测试的话,应该还是 mocha + should + istanbul 吧。
回复
- 描述性弱是设计的初衷不一样的,而 describe it这种属于bdd风格,此时pk的应该是https://github.com/sheerun/ava-spec
- 全都可以独立执行,好处是测试速度会比较快,缺点测试写的时候要提前规避,当然这是好习惯的,不过对于遗留系统的测试,还是慎用吧,确实工作量比较大
- ava断言可以随便玩,默认的其实也是借鉴了各大框架里比较好的实践的,不好写倒不至于
- 最后,你没有用ava玩generator和async/await来测试,所以感觉不太明显的,哈哈