- Introduction
- 1. Nodejs入门
- 2. Koa入门
- 3. Koa进阶
-
4.
Koa与数据库
- 4.1. mongodb安装
- 4.2. 了解mvc里m的作用,以及什么样的代码该放到模型里
- 4.3. mongoose入门
- 4.4. 扩展mongoose模型statics方法和methods的区别
- 4.5. 虚拟属性
- 4.6. 回调:pre和post的差别
- 4.7. mongoose的插件机制
- 4.8. mongoose+promise
- 4.9. mongoosedao
- 4.10. 分页
- 4.11. 关系(1对1,1对多)在mongoose里如何实现
- 4.12. AGGREGATION 关联
- 4.13. 了解索引
- 4.14. 了解优化
- 4.15. mongooseconnection
- 4.16. 了解mongodb的部署与部署
- 4.17. UserModel
- 4.18. 随堂练习:完善用户注册、登录、管理
- 5. 从0开始写一个基于Koa的web框架
- 6. 项目实战
- 7. 部署
- Published with GitBook
session
什么是session
http是无状态的
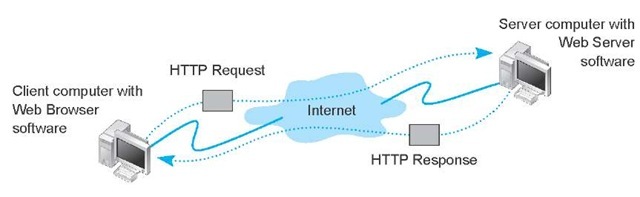
但是服务器可以通过session来保存状态
为什么需要session
一般是在web应用的背景之下,我们知道web应用是基于HTTP协议的,而HTTP协议恰恰是一种无状态协议。也就是说,用户从A页面跳转到B页面会重新发送一次HTTP请求,而服务端在返回响应的时候是无法获知该用户在请求B页面之前做了什么的。
对于HTTP的无状态性的原因,相关RFC里并没有解释,但联系到HTTP的历史以及应用场景,我们可以推测出一些理由:
- 设计HTTP最初的目的是为了提供一种发布和接收HTML页面的方法。那个时候没有动态页面技术,只有纯粹的静态HTML页面,因此根本不需要协议能保持状态;
- 用户在收到响应时,往往要花一些时间来阅读页面,因此如果保持客户端和服务端之间的连接,那么这个连接在大多数的时间里都将是空闲的,这是一种资源的无端浪费。所以HTTP原始的设计是默认短连接,即客户端和服务端完成一次请求和响应之后就断开TCP连接,服务器因此无法预知客户端的下一个动作,它甚至都不知道这个用户会不会再次访问,因此让HTTP协议来维护用户的访问状态也全然没有必要;
- 将一部分复杂性转嫁到以HTTP协议为基础的技术之上可以使得HTTP在协议这个层面上显得相对简单,而这种简单也赋予了HTTP更强的扩展能力。事实上,session技术从本质上来讲也是对HTTP协议的一种扩展。
总而言之,HTTP的无状态是由其历史使命而决定的。但随着网络技术的蓬勃发展,人们再也不满足于死板乏味的静态HTML,他们希望web应用能动起来,于是客户端出现了脚本和DOM技术,HTML里增加了表单,而服务端出现了CGI等等动态技术。
而正是这种web动态化的需求,给HTTP协议提出了一个难题:一个无状态的协议怎样才能关联两次连续的请求呢?也就是说无状态的协议怎样才能满足有状态的需求呢?
此时有状态是必然趋势而协议的无状态性也是木已成舟,因此我们需要一些方案来解决这个矛盾,来保持HTTP连接状态,于是出现了cookie和session。
功能
- 注册
- 登录
- 首页
- 如果已登录
- 如果未登录
koa实现
https://github.com/koajs/generic-session
- 定义sessionStore
- 各种数据库的实现
需要区分
- session
- generic-session
- generic-session具体实现,如
- koa-redis to store your session data with redis.
- koa-mysql-session to store your session data with MySQL.
- koa-generic-session-mongo to store your session data with MongoDB.
- koa-pg-session to store your session data with PostgreSQL.
- koa-generic-session-rethinkdb to store your session data with ReThinkDB.
- koa-sqlite3-session to store your session data with SQLite3.
准备
npm i -S mongoose bluebird
npm i -S koa-generic-session koa-generic-session-mongo
提示,当发现bcrypt无法安装的时候
> bcrypt@0.8.7 install ~/workspace/github/mongoose-base-user-plugin/node_modules/bcrypt
> node-gyp rebuild
gyp: ~/.node-gyp/4.4.5/common.gypi not found (cwd: ~/workspace/github/mongoose-base-user-plugin/node_modules/bcrypt) while reading includes of binding.gyp while trying to load binding.gyp
gyp ERR! configure error
gyp ERR! stack Error: `gyp` failed with exit code: 1
gyp ERR! stack at ChildProcess.onCpExit (~/.nvm/versions/node/v4.4.5/lib/node_modules/npm/node_modules/node-gyp/lib/configure.js:343:16)
gyp ERR! stack at emitTwo (events.js:87:13)
gyp ERR! stack at ChildProcess.emit (events.js:172:7)
gyp ERR! stack at Process.ChildProcess._handle.onexit (internal/child_process.js:200:12)
gyp ERR! System Darwin 14.5.0
gyp ERR! command "~/.nvm/versions/node/v4.4.5/bin/node" "~/.nvm/versions/node/v4.4.5/lib/node_modules/npm/node_modules/node-gyp/bin/node-gyp.js" "rebuild"
gyp ERR! cwd ~/workspace/github/mongoose-base-user-plugin/node_modules/bcrypt
gyp ERR! node -v v4.4.5
gyp ERR! node-gyp -v v1.0.3
gyp ERR! not ok
npm ERR! Darwin 14.5.0
npm ERR! argv "~/.nvm/versions/node/v4.4.5/bin/node" "~/.nvm/versions/node/v4.4.5/bin/npm" "i"
npm ERR! node v4.4.5
npm ERR! npm v2.10.1
npm ERR! code ELIFECYCLE
npm ERR! bcrypt@0.8.7 install: `node-gyp rebuild`
npm ERR! Exit status 1
npm ERR!
npm ERR! Failed at the bcrypt@0.8.7 install script 'node-gyp rebuild'.
npm ERR! This is most likely a problem with the bcrypt package,
npm ERR! not with npm itself.
npm ERR! Tell the author that this fails on your system:
npm ERR! node-gyp rebuild
npm ERR! You can get their info via:
npm ERR! npm owner ls bcrypt
npm ERR! There is likely additional logging output above.
解决方案
rm -rf ~/.node_gyp
核心代码
引用
const session = require('koa-generic-session')
const MongoStore = require('koa-generic-session-mongo')
核心代码
app.keys = ['keys', 'keykeys'];
app.use(session({
store: new MongoStore({
url: require('./mongodb').url(),
ttl: 6000
})
}));
这样是全局的使用session,在后面的中间件里可以使用ctx.session,如果想定制高效,可以在具体路由里使用该session中间件,而非全局。
用法
比如注册
// 注册信息保存
router.post('/register', ctx => {
console.log(ctx.request.body)
var session = ctx.session
let body = ctx.request.body
let user = new User({
username: body.name,
password: body.password
})
return user.save(function(err, doc){
if (err) {
return ctx.redirect('/404')
}
session.current_user = {
username: body.name,
password: body.password
}
return ctx.redirect('/')
})
})
- ctx.session是之前加了session中间件的原因才有的
- ctx.session是一个对象,只要你赋值了,它就会存在
- 这里给session增加了一个current_user对象
- 最后重定向到根路径
然后在其他中间件里即可,获取通过session来共享current_user对象,达到了状态保存的目的。
但session是有时效的,根据ttl设置自动销毁,比如tomcat的默认时间是30分钟,这个可以酌情设置。当session失效,就变成游客模式。
既然session是一个对象,可以挂无数东西,那么是不是什么都可以挂呢?session如果使用cookie存,是内存模式,如果东西太多,会内存爆掉,如果使用db存储(redis或mongodb),就没有这样的问题,但仍然会占用较多,所以。。。除非必要,尽量少在session上放东西。
以前的购物车是放到session里,但真正的电商购物车早已经不用session里,而是持久化。所以目前来看除了和用户登录相关的,很少会用到session。